150+ Fast Food Trivia Questions to Supercharge Your Foodie IQ!
150+ Fast Food Trivia Questions to Supercharge Your Foodie IQ!
Dive into the delicious world of fast food trivia with our mouth-watering collection of over 150 questions! Perfect for quiz nights or to test your own knowledge, these fast food trivia challenges cover everything from iconic burgers to secret menu items. Get ready to indulge in the ultimate foodie quiz experience!

150+ Fast Food Trivia Questions
1. What year was McDonald's founded?
Answer: 1940
2. Which fast food chain is known for its "Whopper" burger?
Answer: Burger King
3. In which city was the first KFC opened?
Answer: Salt Lake City, Utah
4. What is the main ingredient of Subway's Veggie Delite sandwich?
Answer: Vegetables
5. Which fast food chain uses the slogan "Eat Fresh"?
Answer: Subway
6. What is the name of Taco Bell's signature hot sauce?
Answer: Fire Sauce
7. How many herbs and spices are in KFC's original recipe?
Answer: 11
8. What fast food chain has a mascot named Ronald McDonald?
Answer: McDonald's
9. In what country did the fast food chain Domino's Pizza originate?
Answer: United States
10. What year did the first In-N-Out Burger open?
Answer: 1948
11. What fast food chain is known for its Frosty dessert?
Answer: Wendy's
12. What is the name of Starbucks' size larger than "grande"?
Answer: Venti
13. What fast food chain introduced the Big Mac?
Answer: McDonald's
14. Which fast food chain has a secret menu item called "Animal Style" fries?
Answer: In-N-Out Burger
15. What is the main ingredient in a Chick-fil-A chicken sandwich?
Answer: Chicken Breast
16. Which fast food chain was the first to offer a drive-thru service?
Answer: Red's Giant Hamburg
17. What pizza chain is known for its stuffed crust pizza?
Answer: Pizza Hut
18. What year was Pizza Hut founded?
Answer: 1958
19. Which fast food chain has a bell as its logo?
Answer: Taco Bell
20. What is the name of the McDonald's breakfast sandwich that features an English muffin?
Answer: Egg McMuffin
21. What fast food chain is known for its "Blizzard" dessert?
Answer: Dairy Queen
22. Which fast food chain offers the "Famous Bowl"?
Answer: KFC
23. In what year was Wendy's founded?
Answer: 1969
24. What fast food chain is known for its square hamburgers?
Answer: Wendy's
25. What item did McDonald's introduce in 1983 that was a departure from its usual menu?
Answer: Chicken McNuggets
26. What fast food chain is famous for its curly fries?
Answer: Arby's
27. Which fast food chain has a mascot named "The King"?
Answer: Burger King
28. In what country was the fast food chain Subway founded?
Answer: United States
29. What is the slogan of KFC?
Answer: "Finger Lickin' Good"
30. What fast food chain introduced the concept of Happy Meals?
Answer: McDonald's
31. What item is Dunkin' (formerly Dunkin' Donuts) best known for?
Answer: Donuts
32. Which fast food chain offers the "Cinnamon Twist" dessert?
Answer: Taco Bell
33. What year did Starbucks open its first store?
Answer: 1971
34. What fast food chain is known for its "Double Down" sandwich?
Answer: KFC
35. Which fast food chain is famous for its root beer floats?
Answer: A&W
36. In which year did the first Chipotle Mexican Grill open?
Answer: 1993
37. What is the name of the McDonald's product that is a pie filled with apple?
Answer: Apple Pie
38. What fast food chain has a menu item called "The Whataburger"?
Answer: Whataburger
39. Which fast food chain is known for its "ButterBurgers"?
Answer: Culver's
40. What fast food chain introduced the "Crunchwrap Supreme"?
Answer: Taco Bell
41. Which fast food chain was founded by Colonel Harland Sanders?
Answer: KFC
42. What is the name of Dairy Queen's soft serve dessert that is served upside down?
Answer: Blizzard
43. What year was the first Dunkin' Donuts opened?
Answer: 1950
44. Which fast food chain has a mascot named "Jack" with a large ping pong ball-like head?
Answer: Jack in the Box
45. What fast food chain offers a sandwich called "The Big Zax Snak"?
Answer: Zaxby's
46. What is the main ingredient in a Popeyes' famous chicken sandwich?
Answer: Chicken Breast
47. Which fast food chain introduced the "Frappe" to its menu in 2010?
Answer: McDonald's
48. What fast food chain has a logo that includes two
golden arches?
Answer: McDonald's
49. What year did the first Five Guys location open?
Answer: 1986
50. Which fast food chain is known for its "Chalupa"?
Answer: Taco Bell
51. Which fast food chain is known for its slogan "Have it your way"?
Answer: Burger King
52. What is the name of the soft taco shell filled with cheese between two hard taco shells offered by Taco Bell?
Answer: Cheesy Gordita Crunch
53. In what year did Chipotle Mexican Grill begin offering sofritas as a protein option?
Answer: 2014
54. What fast food chain introduced the Pretzel Bacon King sandwich?
Answer: Burger King
55. Which fast food chain is famous for its "Footlong" sandwiches?
Answer: Subway
56. What is the name of Starbucks' pumpkin-flavored seasonal latte?
Answer: Pumpkin Spice Latte
57. Which fast food chain introduced a sandwich called the McRib?
Answer: McDonald's
58. What fast food chain offers a box meal known as the "4 for $4"?
Answer: Wendy's
59. What year was Carl's Jr. founded?
Answer: 1941
60. Which fast food chain is known for its "P'Zone," a type of calzone?
Answer: Pizza Hut
61. What fast food chain uses the slogan "Better Ingredients. Better Pizza."?
Answer: Papa John's
62. Which chain is known for its humorous and often provocative billboard advertisements?
Answer: Chick-fil-A
63. What fast food chain offers a breakfast item called the "Croissan'wich"?
Answer: Burger King
64. What is the name of the Chipotle Mexican Grill dish that is a burrito without the tortilla, served in a bowl?
Answer: Burrito Bowl
65. In which year did Shake Shack begin as a hot dog cart in Madison Square Park?
Answer: 2001
66. What fast food chain is known for its "Grilled Cheese Burrito"?
Answer: Taco Bell
67. What is the name of the coffee-based drink that combines espresso with frothy milk, popular at Starbucks?
Answer: Cappuccino
68. Which fast food chain introduced a plant-based burger called the "Impossible Whopper"?
Answer: Burger King
69. What is the primary meat used in Arby's sandwiches?
Answer: Roast Beef
70. Which fast food chain has a mascot named "The Noid" that was used in their advertising campaigns?
Answer: Domino's Pizza
71. What year did the first Sonic Drive-In open?
Answer: 1953
72. What fast food chain is known for its "Jamocha Shake"?
Answer: Arby's
73. Which fast food chain offers a breakfast menu item called "Cinnabon Delights"?
Answer: Taco Bell
74. In what year was the first Panera Bread (originally St. Louis Bread Co.) opened?
Answer: 1987
75. What fast food chain introduced "Fresco Style" menu options for a healthier choice?
Answer: Taco Bell
76. Which fast food chain is known for its "Dave's Single" hamburger?
Answer: Wendy's
77. What is the name of Little Caesars' deep-dish pizza that is wrapped with 3.5 feet of bacon?
Answer: Bacon Wrapped Deep! Deep! Dish
78. Which fast food chain uses a mascot named "Cuppy," a cup of frozen yogurt?
Answer: Orange Leaf
79. What year did the fast food chain Five Guys begin offering milkshakes?
Answer: 2014
80. Which fast food restaurant is known for its "Chickenjoy"?
Answer: Jollibee
81. What is the slogan of Little Caesars?
Answer: "Pizza! Pizza!"
82. Which fast food chain introduced the concept of ordering pizza by the slice?
Answer: Sbarro
83. What fast food chain has a menu item called a "Frosty-ccino"?
Answer: Wendy's
84. In which country did the fast food chain Jollibee originate?
Answer: Philippines
85. What fast food chain offers a product known as "Crinkle Fries"?
Answer: Shake Shack
86. What year was the first Del Taco restaurant opened?
Answer: 1964
87. Which fast food chain is known for its "Chocolate Frosty"?
Answer: Wendy's
88. What is the name of the signature sauce served with Chick-fil-A sandwiches?
Answer: Chick-fil-A Sauce
89. Which fast food chain has a mascot that is a smiling star wearing sunglasses?
Answer: Carl's Jr.
90. What fast food chain introduced the "Naked Chicken Chalupa," which uses fried chicken as a shell?
Answer: Taco Bell
91. What is the name of the pizza that Domino's Pizza introduced in 2011, featuring a garlic-seasoned crust filled with cheese?
Answer: Stuffed
Cheesy Bread
92. Which fast food chain is known for its "Buttermilk Crispy Tenders"?
Answer: McDonald's
93. What year did the fast food chain Popeyes Louisiana Kitchen open?
Answer: 1972
94. What fast food chain offers a sandwich known as the "Ultimate Cheeseburger"?
Answer: Jack in the Box
95. Which fast food chain has a menu item called "The Charbroiled Atlantic Cod Fish Sandwich"?
Answer: Carl's Jr.
96. What is the name of the Taco Bell menu item that is a taco with a shell made entirely of fried chicken?
Answer: Naked Chicken Taco
97. In what year did the fast food chain In-N-Out Burger introduce its first Secret Menu?
Answer: The Secret Menu has been an unofficial feature for decades, without a specific introduction year.
98. Which fast food chain is known for its "Sourdough Jack" sandwich?
Answer: Jack in the Box
99. What fast food chain offers a box meal known as the "Big Box Meal"?
Answer: KFC
100. What is the name of the breakfast item at McDonald's that combines pancakes and sausage?
Answer: McGriddles
101. What fast food chain introduced the "Fiesta Taco Salad"?
Answer: Taco Bell
102. In what year was the fast food chain Dairy Queen founded?
Answer: 1940
103. Which fast food chain is known for its "Big Catch" fish meal?
Answer: Long John Silver's
104. What is the name of the signature spicy chicken sandwich at Wendy's?
Answer: Spicy Chicken Sandwich
105. Which fast food chain offers a unique menu item called "Mac n' Cheetos"?
Answer: Burger King
106. What fast food chain is famous for its biscuits and uses the slogan "Made from Scratch"?
Answer: Hardee's
107. In which year did Subway start serving breakfast nationwide in the U.S.?
Answer: 2010
108. What is the name of the McDonald's salad that includes kale as an ingredient?
Answer: Kale Caesar Salad
109. Which fast food chain introduced a vegetarian burger called the "Beyond Famous Star"?
Answer: Carl's Jr.
110. What fast food chain is known for its slogan "We Have The Meats"?
Answer: Arby's
111. What year was the first Papa John's pizza restaurant opened?
Answer: 1984
112. Which fast food chain offers "Lil' Donuts" as a dessert option?
Answer: Tim Hortons
113. What fast food chain introduced the "Quesalupa," which features a cheese-stuffed shell?
Answer: Taco Bell
114. In what year did Chick-fil-A introduce its first breakfast menu?
Answer: 1986
115. What is the name of the Starbucks drink that combines espresso, milk, and a hint of caramel?
Answer: Caramel Macchiato
116. Which fast food chain is famous for its "Box Combo," including chicken fingers, coleslaw, fries, and Texas toast?
Answer: Raising Cane's
117. What fast food chain introduced the "Pretzel Bacon Pub Cheeseburger"?
Answer: Wendy's
118. In which country was the coffee chain Tim Hortons founded?
Answer: Canada
119. What year did the fast food chain Bojangles' Famous Chicken 'n Biscuits open?
Answer: 1977
120. Which fast food chain offers a breakfast burrito called the "Loaded Breakfast Burrito"?
Answer: Jack in the Box
121. What is the name of the KFC sandwich that replaces the bun with two pieces of chicken?
Answer: Double Down
122. Which fast food chain introduced the "Firecracker Chicken Wrap"?
Answer: Panda Express
123. What fast food chain is known for its "Butterfly Shrimp Tackle Box"?
Answer: Popeyes
124. In what year did the fast food chain Culver's introduce its first "Concrete Mixer"?
Answer: 1984
125. What is the name of the Taco Bell menu item that combines a taco with a quesadilla?
Answer: Quesarito
126. Which fast food chain introduced a menu item called the "Homestyle Ranch Chicken Club"?
Answer: Jack in the Box
127. What fast food chain offers a product called "Mozzarella Sticks"?
Answer: Sonic Drive-In
128. What year was the fast food chain Del Taco founded?
Answer: 1964
129. Which fast food chain is known for its "Crispy Colonel Sandwich"?
Answer: KFC
130. What is the name of the Starbucks size that is smaller than "Tall"?
Answer: Short
131. Which fast food chain offers the "Steakhouse King" burger?
Answer: Burger King
132. In what year did the fast food chain In-N-Out Burger start offering a "Protein Style" burger?
Answer: The "Protein Style" burger has been a part of the secret menu for many years, without a specific introduction year.
133. What fast food chain is known for its "Peppercorn Mushroom Swiss" burger?
Answer: Wendy's
134. Which fast food chain introduced the "Toasted Cheddar Chalupa"?
Answer: Taco Bell
135. What fast food chain offers a unique side dish called "Red Beans and Rice"?
Answer: Popeyes
136. In what year was the fast food chain Sonic Drive-In founded?
Answer: 1953
137. What is the name of the McDonald's menu item that combines soft serve ice cream with a variety of toppings?
Answer: McFlurry
138. Which fast food chain is famous for its "Cheese Curds"?
Answer: Culver's
139. What fast food chain introduced the "Zinger" chicken sandwich?
Answer: KFC
140. What is the name of the Taco Bell drink that blends Mountain Dew with tropical flavors?
Answer: Mountain Dew Baja
Blast
141. Which fast food chain offers a dessert called the "Oreo Shake"?
Answer: Burger King
142. In which country was the fast food chain Nando's founded?
Answer: South Africa
143. What year did the fast food chain White Castle, known as the world's first fast food chain, open?
Answer: 1921
144. Which fast food chain is known for its "Original Slider" burger?
Answer: White Castle
145. What fast food chain introduced a breakfast option called the "Baconator Breakfast Sandwich"?
Answer: Wendy's
146. What is the name of the Domino's Pizza crust option that is seasoned with garlic and parmesan?
Answer: Garlic Parmesan Crust
147. Which fast food chain offers a menu item called the "Big Box Meal," including a variety of their signature products?
Answer: KFC
148. In what year did the fast food chain Shake Shack begin offering chicken sandwiches?
Answer: 2015
149. What is the name of the Subway sandwich that includes meatballs and marinara sauce?
Answer: Meatball Marinara
150. Which fast food chain is famous for its "Grande Scrambler Burrito"?
Answer: Taco Bell
Congratulations on completing this savory journey through fast food trivia! Whether you aced the quiz or learned something new, we hope these questions added some flavor to your day. Keep this collection handy for your next trivia night and impress your friends with your fast food knowledge. Until then, stay curious and hungry for more!
Get started today for as little as 5.5 cents per word.
The Ultimate Guide to E-E-A-T in 2023 (+ Free Checklist!)
The Ultimate Guide to E-E-A-T in 2023 (+ Free Checklist!)
EEAT – Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness – has become a central pillar of website success in 2023.
This hunger-inducing acronym represents Google’s approach to determining how reliable a particular website is.
The more reliable Google thinks your website and content are, the easier it’ll be to rank high in the search results.
(To read Google’s EEAT guidelines firsthand, you can jump to page 26 of their Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines.)
Unfortunately, Google’s EEAT guidelines are a bit vague, and they don’t provide much actionable advice about how the average website owner can alter their site to meet their expectations.
Enter Kyle Roof – the SEO industry’s leading expert on cracking Google’s EEAT code.
Kyle has recently been interviewed on a series of podcasts to discuss the latest changes to EEAT.
-
-
- Niche Pursuits Interview (January 4th, 2023)
- Income School Interview (January 17th, 2023)
- Authority Hacker Interview (February 13th, 2023)
-
In these podcasts, he provides an awesome overview of what Google is looking for from website owners.
However, much of what he discusses is theoretical – he doesn’t provide many in-depth tips or step-by-step instructions on how to implement these critical EEAT improvements.
To fill that void, I’ve picked up where Kyle left off and written this complete guide to EEAT in 2023.
I’ve included every single tidbit Kyle discusses on these podcasts – as well as additional research from other sources and my own personal experience – and provided actionable, in-depth, step-by-step advice on how to implement EEAT best practices on your website.
Before we get started, make sure you download our complete EEAT checklist!
Download your free printable 2023 EEAT Checklist now.
Alright, let’s dive in.
A Necessary Shift in Perspective
Before I get into the nitty-gritty details, I want to briefly discuss a necessary shift in perspective that I feel many website owners need to embrace.
In Google’s eyes, you’re not just “running a website.”
You’re running a business. And that’s how you should look at this.
You’re earning money through ads, affiliate marketing, and potentially other methods. Because money is involved, you need to look as legitimate as possible.
You can’t hide behind anonymity anymore. You need to put in the work to show Google this is a legitimate business and that a real person is responsible for the website and the content.
You also shouldn’t think of EEAT as an “all-or-nothing” approach. It’s about ticking off as many EEAT boxes as possible to improve your standing in Google’s eyes.
With that, let’s discuss some actionable ways you can implement the first “E” – Experience – on your website.
Experience
According to Google, experience is “the extent to which the content creator has the necessary first-hand or life experience for the topic”
It’s essentially referring to the time you’ve put into learning about the topic and the personal experience you’ve developed as you’ve done so.
So, how do you prove to the Google bot that you have experience?
Kyle believes Google is looking for specific wording and phrases to identify experience. It wants to see that you’re phrasing things in a way that shows you have personal experience with what you’re talking about.
By changing up how you’re writing, you can boost Google’s perception of your site’s experience without having to spend years building real experience in your niche.
Here are a few ways you can do this:
Include Terms That Reference Length of Time and Personal Experience
This is applicable to your About pages and Author bios.
Even if you don’t have much experience in your niche, you can still say things like, “I’ve been in love with skiing for over 30 years. In 1987, I went to Lake Tahoe with my parents, and I’ll never forget flying down the mountains on my brand-new skis.”
Even if that Lake Tahoe trip was the only time you ever went skiing, it’s still a truthful statement. And it adds the time-referencing phrases – “over 30 years” / “In 1987” – that the Google bot is looking for.
Use First-Person and Explain How You Feel About The Topic
Use “I” to explain things in a way that shows you have personal experience with the topic.
Here are a few examples:
| No Evidence of Experience | Evidence of Experience |
| “Cedar is the best wood for this project.” | “I think cedar is the best wood for building a dresser.” |
| “This bike is really heavy.” | “When I picked up the bike, I felt it was heavy and hard to carry.” |
| “This chair is very affordable.” | “After comparing the cost to the competition, I feel this chair is very affordable.” |
Of course, if you don’t have the personal experience these phrases indicate, it’s understandable that you might not want to include these types of phrases.
If you’re concerned about that and want to put forward an honest representation of your experience, I would still suggest using these phrases where you can. Many such phrases are valid and honest even if you haven’t personally experienced what the article is discussing.
For example, the first and third examples in the above table would be valid even if you’ve only done internet research on the topic. You can think that cedar is the best wood for building a dresser without actually having built a dresser.
Expertise
According to Google, Expertise is: “The extent to which the content creator has the necessary knowledge or skill for the topic.”
Here’s the kicker, though: with the exception of YMYL pages, you don’t need to be an expert to rank.
According to Kyle, all Google really cares about is that a real person is behind the content.
Of course, listing certifications and degrees is helpful. But it’s not required.
Let’s dive into some specific actions you can take to boost your site’s Expertise.
Create Author Bio Pages
Each author on your website should have a page with their name, photo, and a few paragraphs listing relevant information about them. This information might include:
-
-
- Their experience in the niche
- Other websites or publications they’ve written for.
-
You’ll want to write as much as possible about your (or your authors’) experience with and passion for the niche. If it feels salesy and boastful, that’s a good thing. (This will help establish trust with your audience as well.)
It also helps to publish pictures and videos of you participating in your niche.
Have a horse website? Add a picture of you on a horse!
Even if you don’t participate with your niche at all, you should – if possible – get a few pictures of you interacting with your niche in some capacity.
Pro-tip: Make sure you link to the author bio page from the About the team page (and vice-versa).
Use Person Schema
Schema is a special type of HTML code that makes it easy for search engines to detect certain things about your content.
When setting up your Author Bio pages, you’ll want to implement person schema so you can feed the Google bot valuable EEAT-boosting information.
Here’s some of the information person schema lets you give to the Google bot:
-
-
- Name
- Short bio (Include alumni information if possible)
- Email address
- Physical address
- Gender
- Job title
- SameAs links (LinkedIn page, other social media profiles, and other related websites).
-
Some themes already have person schema built-in, while others will require you to use an SEO plugin like RankMath or AIOSEO to implement it on a specific page.
Check your theme’s documentation (or just Google your theme’s name + “person schema”) to see if you’ll need to use one of these plugins to implement person schema.
-
-
- Here are instructions for adding person schema to a page using RankMath.
- Here are instructions for adding person schema to a page using AIOSEO.
-
If you want to make things super easy, you can use the Schema Pro plugin to implement all types of schema markup in just a few clicks.
It's not cheap at $67 per year, but it might be worth it if you don't want to work through the extra complexities involved in the free tools.
Note: Listing your social profiles is about establishing you’re a real human, not that you’re an expert.
Use Article Schema
Article schema makes it easier for Google to understand essential information about your articles, including:
-
-
- Article title
- Date the article was published
- Featured image
- Meta description
- Link to author’s bio
-
Again, your theme may include this already. If it doesn’t, you’ll need a plugin like RankMath or AIOSEO.
-
-
- Here are instructions for adding article schema using RankMath.
- Here are instructions for adding article schema using AIOSEO.
-
Leverage User-Generated Content (UGC)
Google loves user-generated content.
They mention in multiple documents that UGC can help improve their evaluation of a given page (and help you perform better in the SERP).
In the context of blogs, utilizing the power of UGC means allowing comments from your readers.
Their thinking is that a “go-to source” for information in a given niche would likely have comments from readers asking for advice and clarification.
While many SEO professionals recommend disabling comments – after all, it takes work to moderate and respond to them – Google encourages you to enable them.
Over time, the accumulation of comments from interested readers – and your responses to those comments – can add valuable insights that weren’t included in the original article.
Not only does this add value to the article, but it allows you to passively “update” your posts with new content as new comments are added.
It also creates a “moat” around your content that is difficult for your competition to cross.
Competitors who want to compete with you for a given search query will have a harder time outranking you if you have dozens of comments from readers sharing additional information and asking questions that you didn’t cover in the initial article.
If you compare two articles of similar length and content coverage – but one has 2,000 additional words of comments from readers – Google will view the article with comments more favorably.
Pro-tip: You can respond to comments with SEO-optimized responses to help you improve your rank for the target search query and rank for additional queries.
Adding a Comments Section to Your Posts
WordPress has built-in comment functionality, and many themes come with a custom comments section.
However, if you’re not happy with the WordPress comments or the functionality included in your theme – third-party plugins can easily insert comments sections that Google can read.
Here are a few free options:
Note: Kyle mentions that you shouldn’t use comments plugins that use Javascript — AKA all of the plugins listed above — as it can make it harder for the Google bot to crawl the comments.
However, I asked technical-wunderkind Josh Koop of WhiteHatBlogging.com about this, and he said it really shouldn’t make a difference because Google always crawls your site twice – once for HTML and once for Javascript.
Given how cool some of these plugins are, I’d personally take the risk and use one of them over the vanilla WordPress comments. But it’s up to you!
Additional Expertise Insights
Here are a couple extra tidbits I’d like to share about the Expertise category:
-
-
- Google does not make value judgements about expertise. A degree from Harvard is viewed the same as a degree from your local community college. Similarly, they view a doctor from America as equivalent to a doctor from another country.
-
-
-
- Some YMYL info and advice must come from an expert. One example given in the search rater guidelines is accounting advice.
-
Authoritativeness
According to Google, authoritativeness is “the extent to which the content creator or the website is known as a go-to source for the topic.”
However, according to Kyle, you don’t need to be an expert to check off the Authoritativeness boxes.
What matters is how thoroughly you’ve covered the topic. And the best way to do that is by building topical authority.
Build Topical Authority
To gauge your site’s topical authority, Google looks at how thoroughly you’ve covered the topic on your website.
To be clear, I’m not talking about writing an extremely comprehensive article about a particular topic.
I’m talking about how thoroughly your site as a whole covers that topic.
Here's an example...
Let’s say you have a website about skis and want to target the sub-niche of cleaning your skis.
You could write an amazing 10,000-word mega-post on how to clean your skis.
But it’ll be hard to rank that article if it’s the only article about cleaning skis on your website!
To show Google that you are an authority on this topic, you should publish content about every corner of the “cleaning skis” sub-niche.
This might include:
-
-
- Types of ski cleaners (liquid, foam, wax, etc.)
- Cleaning equipment (brushes, cloths, scrapers, etc.)
- Proper cleaning technique (removing dirt and debris, cleaning edges and base, drying skis)
- Considerations for different types of skis (e.g. powder skis, racing skis)
-
In each sub-category within the “cleaning skis” sub-niche, you might write several articles that cover all important aspects of the sub-category.
This is what Google wants to see in 2023. Simply cherry-picking low-competition search results isn’t going to cut it moving forward.
Trustworthiness
According to Google, “Trust is the most important member of the E-E-A-T family because untrustworthy pages have low E-E-A-T no matter how Experienced, Expert, or Authoritative they may seem.”
For example, a well-known banking expert could create a page that promotes a financial scam. This page would have extremely low EEAT even though the author is an expert in the topic.
The goal in this phase is to prove you’re a real business. You need to show Google that a real person is responsible for this website and its content.
Get a Unique Business Address
Getting a unique business address is crucial for proving to Google that your website represents a legitimate business venture.
The key word here is unique. Kyle made it clear that you don’t want to share an address with any other businesses.
Note: If you’re targeting a U.S. audience, you’ll want a U.S. address. If you're targeting a different audience, get an address in that country.
(Most websites target a U.S. audience, so these explanations will focus on that. The advice is similar for other countries, though.)
The easiest solution to the address problem – at least for those who live in the United States – is to use your home address.
However, many people understandably don’t want to publish their home address for hundreds of thousands of strangers to read.
If you don’t want to use your home address – or you don’t live in the U.S. – the next best thing is to get a virtual mailbox address.
These services provide you with a real address you can use on your website. They’ll also scan any mail you receive and send it to you digitally.
You’ll want to be careful when selecting a service, as not all of them offer unique suite numbers that differentiate you from the other people using this service.
I did some research and found a couple of services that offer a unique suite number:
-
-
- Sasquatch Mail: $9.99 per month.
- Traveling Mailbox: $15 per month.
-
You don’t need anything fancy here. As long as you get an address with a unique suite number, you’re good to go.
Note: Anyone signing up for a virtual address in the U.S. must sign USPS Form 1583.
If you’re a U.S. resident, you can simply fill this out yourself.
However, if you’re from outside the U.S., you’ll need a notary to sign the form for you. You can easily do this through an online service like OnlineNotary.net.
Once you have your address, you should put it in the footer of your website and on your Contact and About pages.
Get a Unique Phone Number
In addition to a unique address, you’ll also want a unique phone number.
It’s important that this phone number matches the location of your business address. Google might not like it if your business address is in Chicago and you’re using a Seattle phone number.
If you're in the United States, The easiest way to get one is through Google Voice. It's free, and all you’ll need is an existing phone number to link it to.
You can also set it up so that all phone calls are automatically routed to the Google Voice voicemail box.
This lets you review any calls that come in at your leisure and decide which are worth responding to.
Setting up the number is very straightforward, so I won’t explain how to do that here.
However, I will explain how to ensure calls aren’t forwarded to your primary number:
- 1. Go to Google Voice settings.
- 2. Go to the “Incoming calls” section.
- 3. Disable “Web.”
- 4. Disable “Call Forwarding”
If you're not in the United States, you can use a service like Sonetel to claim a number that matches your business address.
Once you’ve done this, you can add your new phone number to your website footer and the Contact and About pages.
Show Your Face
It’s important that a real face belonging to a real person is clearly shown to be responsible for everything on the website.
Kyle gave the example of the Dr. Axe website, which got annihilated a few years ago in a Google update.
While Dr. Axe has legitimate certifications, there was no About info or pictures of him on the site. Because Google couldn’t verify who was responsible for the site, they decided they couldn’t trust it and stopped ranking most of the content.
To cover your bases, you should include multiple photos of yourself (or whoever is representing the site) – at least one on the About page and a separate photo for the Author profile.
Create Multiple Company Email Addresses
Generic contact forms aren’t enough to make Google happy. To satisfy their requirements, you will need to create email addresses for the various “departments” in your company.
I know that most of you only need a single contact email. However, it doesn’t hurt to pretend you have a sprawling company with different departments and create an email address for each one.
Here are a few email addresses you can create:
-
-
- [email protected] (a catch-all email for general inquiries)
- [email protected] (for people who have technical questions about your site)
- [email protected] (for advertising queries)
- [email protected] (for people who want to provide feedback on content)
- Different emails for each author (example: [email protected], [email protected], etc.)
-
Most of these addreses will never be contacted by anyone. However, it’ll make the Google bot like you more, which is all that really matters.
You should be able to create all of these email addresses for free within your web host. Every web host I’ve been with has offered that. If not, Google Workspace is a relatively affordable option.
To keep things simple and ensure you don’t miss out on messages, you can forward all mail to the general contact email.
Submit an XML Sitemap to Google
An XML sitemap is a file that helps Google (and other search engines) find all of the pages on your website.
Having one is essential for ranking on Google. If Google can’t locate your pages, they can’t display them in the search results.
WordPress does automatically generate an XML sitemap for you, so you don’t necessarily need a plugin for it.
However, some technical SEO experts recommend using an XML sitemap from a third-party plugin, as the WordPress plugin is rather basic and might result in Google not crawling every page.
General-purpose SEO plugins like RankMath and AIOSEO can do this for you.
You can also use the XML Sitemaps plugin if you don’t want to use a general-purpose option.
Once you’ve got your sitemap generated, you can submit it to Google through the following process:
- 1. Grab the URL of your sitemap. It should be easily accessible in your sitemap plugin. If you’re using the WordPress sitemap, you can simply use “sitemap.xml”
- 2. Go to Google Search Console.
- 3. Select your website.
- 4. Go to “Sitemaps” on the left-hand sidebar.
- 5. Remove any outdated sitemaps that may already be there.
- 6. Enter the URL of your new sitemap.
Publish an HTML Sitemap
An HTML sitemap is essentially a human-friendly form of XML sitemap.
In case there are issues with Google accessing your XML sitemap, publishing an HTML sitemap provides a failsafe that ensures Google can access all of your pages.
There are a few plugins that will instantly create an HTML sitemap for you:
Once the page has been generated, you should embed it in your site’s footer. This will make it very easy for Google to access it and crawl all of your pages.
Ensure GDPR Compliance
GDPR compliance is important if your website reaches European users (which is pretty much every website).
For a complete guide on making your site GDPR-compliant, I recommend reading this GoDaddy article on Practical steps for Website GDPR compliance.
To keep things simple, I’ll list the two most important steps here:
-
-
- Make sure your privacy policy includes GDPR-compliant language. To ensure you aren’t missing anything, I recommend using a free privacy policy generator like Termly.
- Display a GDPR cookie notification pop-up. The GDPR Cookie Compliance plugin will do this for you automatically.
-
Add an “About the Company” Page
The “About the company” page can have information about how your company got started, your mission, and similar high-minded concepts.
Don’t worry… you don’t have to publish a haughty essay about how you want to change the world with your website.
This can simply be a few paragraphs about why you created your site and how you want to help people learn more about your niche.
Add an “About the Team” Page
The “About the Team” page is where you’ll put all of the humans who work with you.
Include names, photos, titles, and links to each person’s individual bio page.
You should make this page even if you’re the only person on your team.
Add a Privacy Policy
If you don’t have a privacy policy on your site yet, it’s an absolute must-have.
Fortunately, it’s very easy to create. Termly will quickly generate a custom privacy policy that fits your site’s exact specifications.
Add a Terms and Conditions Page
A Terms and Conditions page is just as important as a privacy policy. Google typically won’t even approve your site for ads if you don’t have either of these pages.
Again, you can use Termly to generate one for free.
Add a Refund Policy (if applicable)
If you sell digital or physical products on your site, it’s important to have a page that explicitly explains your refund policy.
Add a Copyright message
You should always have a Copyright message containing your company’s name, the copyright symbol (or the word “Copyright”), and the current year in the footer.
Example: © 2023 | We Write Blog Posts LLC
Enable SSL Certificate
If you haven’t enabled your SSL certificate, you need to do that pronto.
Any decent web host will offer SSL certificates for free. If you need help setting it up, contact your host’s support team.
Check for 404 errors
Google doesn’t like links that don’t go anywhere. If any pages on your site are linking to another page on your site that no longer exists – thereby generating a 404 error – you should find those and fix them.
Here are a few plugins that can help you find them:
Check for broken external links
Google hates when you link out to nonexistent pages on other websites just as much as they hate linking to nonexistent pages on your own site.
The Broken Link Checker plugin is an easy way to find broken external links. This works for 404 errors as well.
Additional Insights
Before I end this post, I want to share a few extra insights I learned that didn’t fit into any of the above sections.
-
-
- Publishing 1,000 articles in a single day is much better than publishing 1 article per day for 1,000 days. It gives Google more time to index and understand your content, and you'll grow your site much faster.
-
-
-
- If you review products, you should make an editorial guidelines page that explains how you perform your product reviews and choose your recommendations. A great example is the Product Research Methodology page from SleepFoundation.org.
-
-
-
- Kyle believes publishing AI content without substantial human editing will be the equivalent of publishing duplicate content. If websites all generate the same articles with ChatGPT, Google will recognize that and penalize all sites publishing that content.
-
-
-
- Kyle believes that if you are going to use AI to create content, you should use it to generate a rough outline and then fill in the blanks with human-written content. Don’t use it to generate the bulk of an article, as you’re running the risk of adding inaccurate information and getting hit for duplicate content.
-
Conclusion
To summarize, here are the strategies you can use to boost your site’s EEAT:
-
-
- Experience
-
- Include terms that reference length of time and personal experience.
- Use first-person and explain how you feel about the topic.
-
- Expertise
-
- Create Author bio pages.
- Use person schema.
- Use article schema.
- Enable (and respond to) comments on your blog.
-
- Authoritativeness
-
- Build topical authority by creating content clusters.
-
- Trustworthiness
-
- Get a unique business address.
- Get a unique phone number.
- Show your face on your site.
- Create multiple company email addresses.
- Submit an XML sitemap to Google.
- Publish an HTML sitemap.
- Ensure GDPR compliance.
- Create an About the Company page.
- Create an About the Team page.
- Add a privacy policy.
- Add a terms and conditions page.
- Add a refund policy (if applicable).
- Add a copyright message.
- Enable an SSL certificate.
- Check for 404 errors.
- Check for broken external links.
-
- Experience
-
And if you haven't already, remember to get your free EEAT checklist!
Download your free 2023 EEAT Checklist now.
Get started today for as little as 5.5 cents per word.
How (And Why) We're Protecting You From AI Content
How (And Why) We're Protecting You From AI Content
At We Write Blog Posts, we’re dedicated to providing a high level of content quality — no matter the challenge.
The recent release of ChatGPT represented the tallest hurdle yet in that pursuit. (I wrote a guide on how ChatGPT works if you want to learn more about it.)
We’re committed to producing 100% human-written content, and we’ve been discussing how to ensure that since ChatGPT was released. This is especially important given how easy it is for writers to make ChatGPT write like a human or train ChatGPT to write like you.
While we have a very high level of trust in our writers — many of whom have been with us for a few years now — we appreciate the need for a process to verify that content isn't being created with the use of AI.
Fortunately, we’ve come up with a solution that involves a really useful tool and careful analysis of how writers add content to their documents.
But before I get to that, I want to briefly explain why simply using one of the AI detection tools that have cropped up recently isn’t the magic bullet it seems to be.
The Hard Truth: AI Detection Tools Suck
Our initial thought when deciding how to deal with AI content was to use one of the AI detection tools that have cropped up recently.
However, our internal tests with tools that supposedly detect AI content have been discouraging, to say the least.
We found that each tool we tried — including Originality.ai, CopyLeaks, Writer.com, and ChatGPT’s AI detector — was woefully inadequate.
They all throw a ton of false positives, and they’re pretty easy to fool by changing the wording of the AI output.
Even OpenAI — the creator of ChatGPT — says their AI detector is only right 26% of the time.
They simply aren’t good enough to be trusted. And this is compounded by how easy it is for writers to make ChatGPT undetectable by AI detectors like TurnItIn and GPTZero.
Therefore, simply telling you, “We’re running all of our articles through an AI detector tool,” and calling it a day would have been a terrible way to approach this.
A Different Approach
Because the AI detection tools suck, our focus shifted from using those tools to evaluating how articles were created by the writers.
Because we use Google Docs to create our content, we started experimenting with looking through Google Docs version histories to check for large sections of text added within an abnormally small timeframe.
If a writer is writing articles normally — by performing proper research and typing the article word-by-word — the Google Docs version history shouldn’t show whole paragraphs or sections added in a single moment (which is what it would show if they pasted in AI-generated text).
Makes sense, right?
Well, it's good in theory, but it doesn't quite work.
The problem with this approach is that the Google Docs version history doesn’t provide enough detail. It only shows changes in batches that update every minute or so.
If someone is a fast typist, it could easily seem like they are pasting in entire paragraphs when they’re just typing efficiently. So simply viewing the version history wasn’t good enough.
Our Solution To The AI Problem
The recent release of a new tool handed us a gift-wrapped solution.
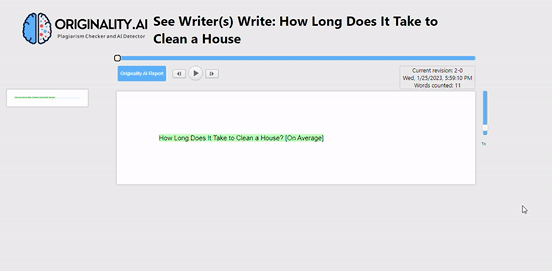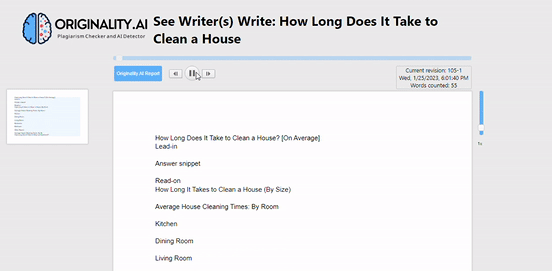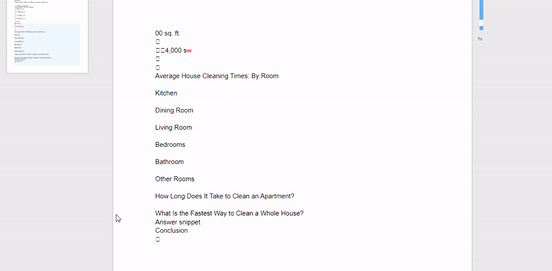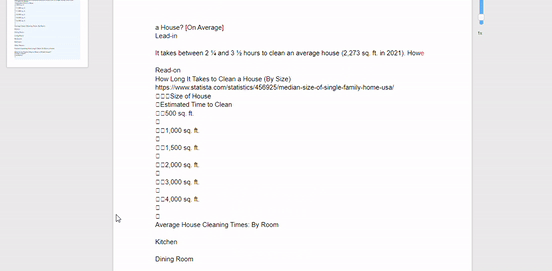
Originality created a Chrome plugin that allows you to view exactly how content written in a Google Doc was added.
It’s like the Google Docs version history tool on steroids.
While Google Docs merely shows a rough outline of edits made within a given period, this tool shows every single character that was added to and removed from the document — all the way from document creation to article completion.
It’s pretty incredible. Here’s a gif that shows how it works:
That’s not all it does, though.
It also provides a graph that displays the character addition trends over time.
This makes it extremely easy to identify when large sections of text are added in a short period.
For example, the graph for an article written normally will look something like this: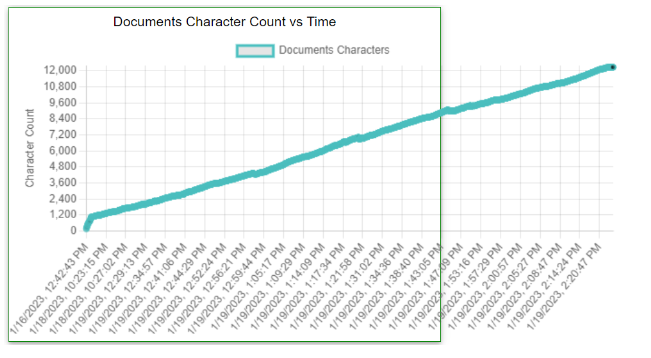
While the graph for an article created with AI might look something like this:
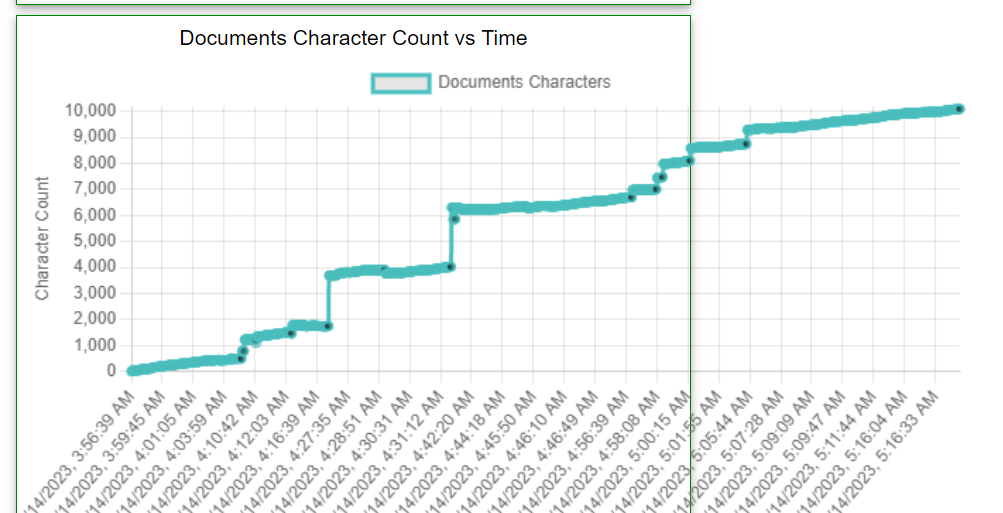
Notice the vertical jumps in character count when large sections of text were pasted into the document.
While there are certainly instances where pasting in text is warranted — such as when you're directly quoting someone — there is no situation in which pasting 2,000+ characters at the same time is okay.
We believe this tool offers the best way to detect and defend against AI usage when outsourcing, and we’ll be incorporating it into our workflow immediately.
How We’ll Use This Tool To Protect You
To make sure we use this tool to its full potential and continue to provide a high level of quality, here’s what we’ll be doing:
- We will review the edit history of every article to check for signs of AI content.
- We will require writers to write each post in a single Google Doc from start to finish. Writers who do not adhere to this requirement will be removed from our team.
- We will continue to require writers to add sources to the sources list as they use them. This makes it easy for us to use this tool to identify where writers are getting their information as they add it to the sources list. (This also allows us to detect AI content even if a writer decides to manually type the AI content into the document rather than pasting it in.)
- Our editors will continue to thoroughly read through articles to check for factual inaccuracies, statements that don’t fit into the context of the article, and other potential signs of AI usage.
Now that I’ve covered how we’ll protect you from AI content, I want to briefly explain why it’s important to avoid AI content in your articles.
Why It’s Important To Defend Against AI Usage
Many people have been concerned about Google detecting and penalizing content created with the help of AI.
Thankfully, Google recently clarified their stance on AI usage in content.
You can read their full statement here, but I can easily summarize it in one sentence:
As long as the content is good, Google doesn’t care how it was made.
If the Google algorithm detects traces of AI usage in your content, it will not automatically penalize your website.
However, despite this clarification, I want to make something clear:
Using AI to generate content is still very risky.
The problem lies in the abundance of incorrect information AI-generated content can contain.
I’ve been researching AI since ChatGPT was released — both in testing it myself and reading about others’ experiences with it.
By and large, the consensus is that it presents information very confidently, but that information is often wrong.
Here are a couple examples of incorrect content:
- ChatGPT generated a recipe for bread that didn’t mention you need to let the bread rise. If you followed the recipe, you’d have been left with an inedible brick. (This link is to a post in the Project 24 community, so if you’re not a member, you won’t be able to view it.)
- Google’s first tech demo of their Bard AI contained an inaccurate statement. It said the James Webb Space Telescope took the first picture of a planet outside our solar system. The first picture was actually taken by a telescope in Chile almost 20 years ago. (Google’s stock price dropped $100 billion after this incident.)
This is why we’ve implemented such stringent anti-AI measures.
The worst thing you can do on your blog is publish inaccurate information, and using AI makes it very difficult to verify that what you’re publishing is true.
Why We Write Blog Posts vs. ChatGPT: Why We’re The Better Choice
Despite the surface-level impressiveness of ChatGPT, it has deep-seated flaws and can’t be trusted to provide accurate information.
A carefully designed content creation process manned by professional writers and editors remains the ideal way to create original, high-quality blog posts.
We’ve taken great care to develop such a process here at We Write Blog Posts. Here are a few measures we take to maintain a high level of quality control.
- Our writers are trained to identify and use information from authoritative sources that can be trusted to provide accurate information.
- We have a strict editorial process where each is closely reviewed by multiple experienced editors. Each article we submit comes with a list of the sources the writer used — our editors use this list to verify that all information comes from a trustworthy source.
- Our editors are trained to examine sources and identify inaccurate information.
Here’s the bottom line: we are fully committed to providing the same original, high-quality content we always have.
The proliferation of AI tools like ChatGPT does not change our mission, and we are confident that the processes we’ve implemented will prevent AI usage in our content.
Before I finish this post, I want to add a quick addendum about the documents we submit to you.
We submit all content to you on a We Write Blog Posts company Google account rather than submitting the writer’s version of the document.
This is to ensure your content remains accessible even if the writer decides to close their Google account or delete their version of the document.
Because of this, if you use the Originality plugin to analyze one of our articles, you’ll see that all of the content was pasted in at once.
This does not mean AI was used to create the article — it’s merely evidence of our editing team transferring the writer’s content to a company-hosted document.
Get started today for as little as 5.5 cents per word.
The Ultimate Guide to Eradicating Spun Content
The Ultimate Guide to Eradicating Spun Content
Spinning is a huge problem in the content creation industry.

But the truth is that sometimes writers can’t help but spin their content.
And nobody likes to talk about it… especially content agencies.
If you — or the writing agency you’re outsourcing with — don’t check their work carefully, you could end up with a website full of spun articles waiting to get hit by a Google update.
And you’d have absolutely no idea.
As the owner of a high-volume content service, I feel I'm in the perfect position to provide some guidance and perspective on this taboo topic.
Here's what I’ll be sharing with you today:
- • What truly constitutes "spun content."
- • The damage spun content can do to your website (with a real-life example).
- • The ins and outs of our anti-spin process (so you can replicate it and make sure you’re not unwittingly buying spun content from other sources).
- • The best spin checking tool available (based on our internal data).
What Is Spun Content?
Before we start this discussion, it's best that I quickly go over the telltale signs of spun content:
- • Similar sentence structure with word choice slightly altered.
- • Similar flow of ideas from sentence to sentence.
- • Similar subheading structure throughout the entire article.
- • Similar information presented in the same order and/or format.
While some minor similarities between articles about similar topics are to be expected — after all, the point of research is to use information from other sources — you shouldn’t see blatantly obvious similarities between multiple sentences, paragraphs, or subheadings.
The writer should be taking any information they use and synthesizing it into a fresh article with a unique, value-adding take on the topic. They should not be copying another person’s sentences and merely rearranging the structure and vocabulary.
The Dangers of Spun Content
Spun content can hurt your site in a few different ways.
Sitewide Google Penalty
If your site has a surplus of spun content on it, you’re at risk of getting whacked by a Google update.
Don’t believe me? Here’s what Google has to say about it in their Spam Policies documentation:
“Some site owners base their sites around content taken ("scraped") from other, often more reputable sites. Scraped content, even from high quality sources, without additional useful services or content provided by your site may not provide added value to users.”
And one example they give of “scraped content” is...
“Sites that copy content from other sites, modify it only slightly (for example, by substituting synonyms or using automated techniques), and republish it.”
So there you have it. Google is telling you that spun content is a problem and can result in a hit to your traffic.
Now, no one knows to what extent an article has to be spun — or what percentage of your published articles need to contain spun content — for Google to annihilate your site and destroy years of painstaking effort.
However, a sitewide Google penalty isn’t the only way spun content can hurt you.
Individual Article Ranking Issues
Google's algorithm may also take an article’s similarity to other published articles into account when deciding where to rank it.
Individual articles with spun sections may not rank well even if your site as a whole has not been penalized. This is because spun content doesn't add any new value or unique perspective, and Google has no reason to rank your article over the other articles that are already providing the same exact information.
If a substantial number of articles contain elements of spinning, you might find your traffic is significantly stunted.
It Damages Your Authority
Spun content can also hurt you from an authority standpoint.
If you’re trying to position yourself as a leading expert in your niche, it’s not a great look if your audience (or other leaders in the niche) discovers you're copying content from other industry experts.
Other authorities in your niche might turn down valuable collaboration opportunities, which can dampen your potential reach and cause you to lose out on valuable backlinks.
You can also lose the trust of your audience, which may have serious consequences for monetization. If you're going to recommend or sell products to your audience, it's imperative that they trust your opinion. If they don't trust you, they're not going to buy your products, and if they're not going to buy your products, you're not going to make money.
How To Detect Spun Content
In my experience, the only way you can effectively detect spinning is to use a multi-step process that includes using a top-notch spin detection tool and manual analysis from a trained editor.
You need both components to feel truly confident in your spin detection capabilities. Leaving out either one leaves you vulnerable to missing something.
Let me explain how you can combine these strategies to create a formidable anti-spin system.
Step 1: Use Spin Checking Software
Your biggest allies in the fight against spinning are spin-detecting software tools.
There are so many potential sources a writer could choose to spin from. Going one by one and manually comparing your article to the countless related articles out there is a time-consuming and ultimately fruitless task.
To find potential issues quickly, you need the help of software tools that can scan billions of web pages in a few seconds.
In my 4+ years of experience writing blog content, I've found 5 popular tools that claim to detect plagiarism and spun content:
To determine which tool is the best for detecting spun content, I ran an experiment. Let's look at the results below.
Experiment Results
In taking on this experiment, I wanted to quantify two things to help us with our approach to spinning:
- • How much spun content we were detecting and rewriting.
- • How effective each tool is at detecting spun content.
Determining Prevalence of Spun Content
Fortunately, the first task was easy.
We keep track of every single piece of spun content we detect. Our data shows that about 4% of all articles that come through our editing queue are at least partially spun.
I also randomly selected 100 unedited articles, ran them through all 5 tools, and manually analyzed any relevant triggers that appeared.
My findings matched our internal data pretty exactly. Out of 100 random unedited articles, I found 4 with clear signs of spinning.
Tool Efficacy Test
To evaluate tool efficacy, I found 30 articles from the last year that we’ve confirmed to be spun and analyzed how effective each tool was at detecting the spun content.
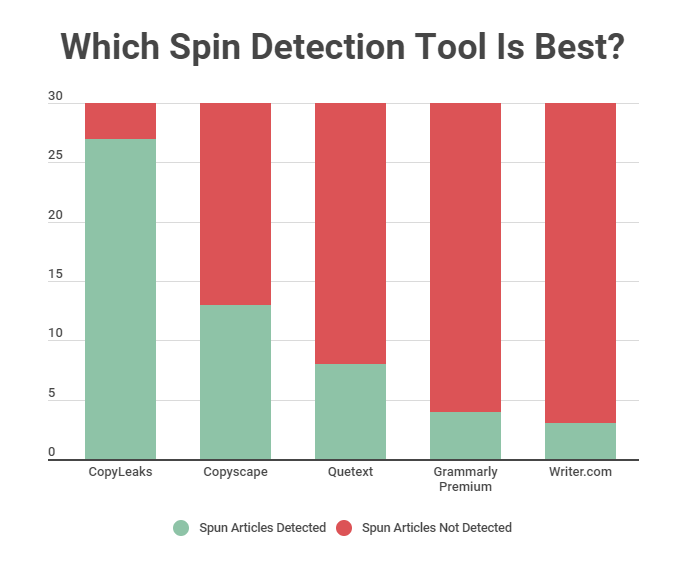
Here are the results:
- • CopyLeaks: Detected 27/30 spun articles.
- • Quetext: Detected 13/30 spun articles.
- • Copyscape: Detected 8/30 spun articles.
- • Grammarly Premium: Detected 4/30 spun articles.
- • Writer.com: Detected 3/30 spun articles.
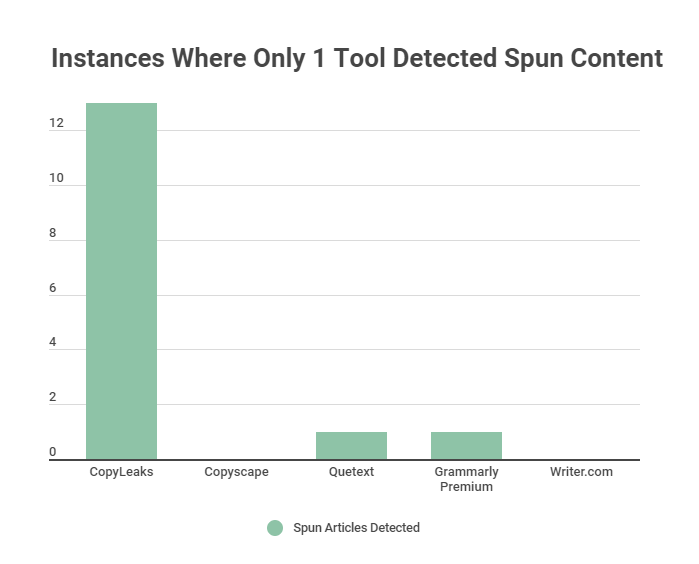
And here’s something pretty interesting: 50% of these were only detected by one tool (CopyLeaks):
- • 13/30 were only detected by CopyLeaks.
- • 1/30 was only detected by Quetext.
- • 1/30 was only detected by Grammarly Premium.
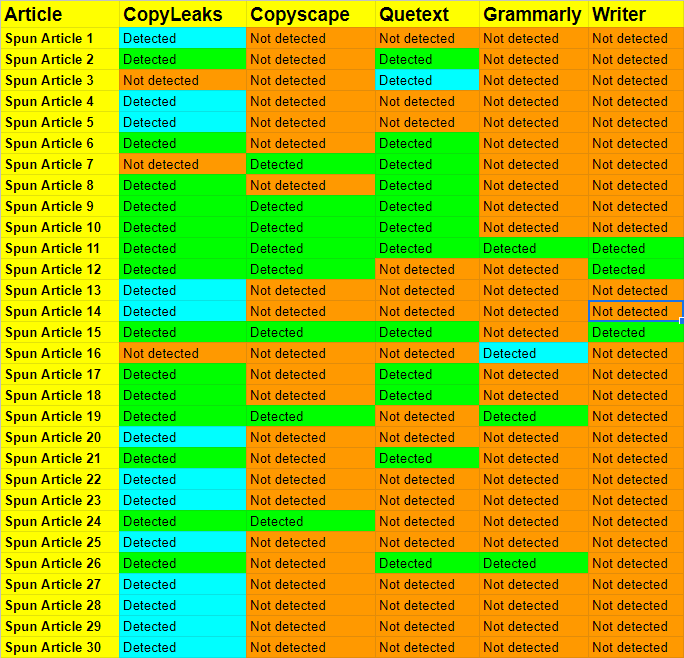
For extra context, here’s a screenshot of the spreadsheet I was working in.
- • Green = Tool detected the spun content.
- • Orange = Tool did not detect the spun content.
- • Cyan = Tool was the only tool to detect the spun content.
The results of this experiment are the reason we've decided to use CopyLeaks as our plagiarism and spin detection software tool.
The other tools clearly show some inaccuracy, and any triggers they did pick up were almost always picked up by CopyLeaks as well.
However, even running your articles through the best spin detection tool out there isn’t enough.
You also need to manually analyze the results and determine if the triggers meet the following criteria:
- • They are relevant to your article.
- • They are actually indicative of spinning.
Dealing with False Positives
Before moving on to the manual analysis, I want to discuss one of the most frustrating things I’ve found with some of these tools: they love to give you false positives.
Two tools in particular — Grammarly Premium and Quetext — are notorious for showing triggers that have absolutely nothing to do with your article.
And when they do provide a relevant trigger, that trigger is often coincidental, and it’s clear the writer didn’t actually reference the article that threw the trigger when they were writing.
Note: When I say “relevant trigger”, I’m referring to a trigger from an article that is about a similar topic.
For example, if I were running an article titled “Why Do Goats Faint?” through Grammarly Premium, I might get the following triggers:
- 1. Trigger from an article about car repair.
- 2. Trigger from an article about goat health.
- 3. Trigger from an article about cats.
In this instance, triggers #1 and #3 are irrelevant because the source articles are about completely different topics. Any similarities are purely coincidental and an example of the plagiarism tool being over-sensitive.
However, trigger #2 is relevant because it’s about the same overarching topic (goats). This would require a manual comparison between the two articles to determine if the trigger is coincidental, or if there are clear signs of spinning.
Analyzing relevant triggers to determine whether they’re spun or not is important. You don’t want to waste a perfectly good article just because a tool says there’s a problem.
In fact, in editing tens of thousands of articles, our team has found that the vast majority of relevant triggers are not evidence of spun content.
They’re simply evidence of the tools being oversensitive and recognizing that articles about similar topics are inevitably going to contain some of the same words.
However, within that high percentage of false positives, you may find a few instances of clearcut spinning, which is why it's important to investigate every relevant trigger you find.
Now that we’ve talked about using tools to identify potential problems, let's discuss how you can analyze each trigger and determine if the content is spun.
Step 2: Analyze Relevant Triggers
If the tools find any relevant triggers, the next step is to compare your article with the article that threw the trigger.
To make the comparison easy, you should mark up your Google Doc with comments that highlight the trigger documents and link to the source.
If you’re using a tool that shows you the specific sentences in the trigger article that caused the trigger to appear — CopyLeaks does this — then you can make it even easier by adding a link directly to the sentence in question.
Here’s how you can do it:
- 1. Go to the web page that caused the trigger.
- 2. Find the sentence(s) that caused the trigger.
- 3. Highlight the sentence(s) with your mouse.
- 4. Right-click the highlighted text and select “Copy link to highlight.”
- 5. Go back to your Google Doc and highlight the text you want to compare.
- 6. Add a comment and paste the link in there.
Now you can easily navigate back and forth between the two articles and quickly analyze them. (Or have a member of your team do it.)
If there are any signs of spinning, they should be easy to detect.
Final Thoughts
Spinning is a common problem when outsourcing, and allowing spun content to reach your website can cause big problems if Google decides to take action.
If you’re only going to use a tool for spin detection, make it CopyLeaks. It’s not perfect, but it’s far better than the other tools out there.
And if you want to breathe easy and avoid worrying about any of this altogether, consider getting your SEO blog content from a service that actually takes spinning seriously.
(Based on our experiment data, any service that is running your content through Copyscape or Grammarly isn't getting the most in-depth spin detection possible.)
Here's the bottom line: Google is upping their game, which means website owners — and content services — need to follow suit. If you don't take steps to ensure you're publishing original content, you may pay a big price for it down the road.
Outsourcing with We Write Blog Posts saves you time and money you’d otherwise be spending checking your outsourced content for spinning.
It also gives you the peace of mind that Google won't smite your site whenever they update their spam detection algorithm.
Our spin defense system is far from the only thing we do to add value to your content, but it is an important protection that — to my knowledge — no other service is currently offering.
If you have any questions about how we can help you scale your website's growth at an affordable price, get in touch with us today.